בחירת חומר פלסטיק
מבוא
אומרים כי יש כ -30,000 עד 35,000 תרכובות פלסטיק בשוק, בעוד פוסט זה נכתב מתווספות עוד ועוד תרכובות כל הזמן.
מספר זה מספיק בכדי לזעזע את הנפש של המעצב המנסה לבחור חומר מיטבי ליישום שלו.
למרבה המזל, רק אחוז קטן מהם הם למעשה מתמודדים רציניים עבור כל יישום נתון.
חלקם פותחו במיוחד עבור מוצר בודד, במיוחד בתעשיית האריזות. אחרים הפכו להיות הבחירה המועדפת עבור יישומים מסוימים בגלל תכונות מיוחדות שהם מציעים ואשר נדרשים עבור אותו מוצר או תהליך.
לדוגמה, הרוב המכריע של חלקים מיוצרים בטכנולוגיית תבנית מסתובבת, עשויים פוליאתילן, בעוד פוליאסטר מחוזק בסיבי זכוכית הוא סוס העבודה של תעשיית הטרמוסטים.
קצת מחקר נדרש בכדי לגלות אם קיים חומר המועדף על כל יישום מוצר נתון.
תרמופלסטיק ותרמוסטיים
First, a bit of a review of the basic categories of plastics materials. In general, they fall into one of two categories: thermosets and thermoplastics. Thermosets undergo a chemical reaction when heated and cannot return to their original state. Consequently, they are chemical resistant and do not burn. Cross-linked plastics are an example of thermosets. Thermoplastics constitute the bulk of the polymers available. Although some degradation does occur, they can be remelted. Most are readily attacked by chemicals and they burn readily
תרמופלסטיק אמורפי וקריסטלי
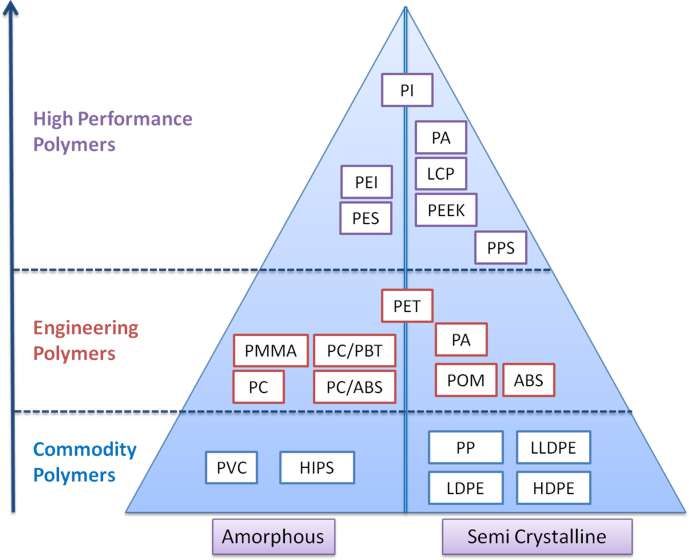
Thermoplastics can also be broken down into two basic categories: amorphous and semicrystalline (hereafter referred to as crystalline). The names refer to their structures; amorphous have molecular chains in random fashion and crystalline have molecular chains in a regular structure. Polymers are considered semicrystalline because they are not completely crystalline in nature. Amorphous resins soften over a range of temperatures whereas crystallines have a definite point at which they melt. Amorphous polymers can have greater transparency and lower, more uniform postmolding shrinkage. Chemical resistance is, in general, much greater for crystalline resins than for amorphous resins, which are sufficiently affected to be solvent welded. The triangle illustrated in Fig. provides an easy way to categorize the thermosplastics
מחיר הפלסטיק
The cost of plastics, generally, increases with a corresponding improvement in thermal properties (other properties, typically, go up as well). The lowest cost plastics are the most widely used. The triangle in Fig. is organized with the least temperature-resistant plastics at the base and those with the highest temperature resistance at the top. Therefore, the plastics designated “Standard” at the base of the triangle, often referred to as commodity plastics, are the lowest in cost and most widely used. They can be used in applications with temperatures up to 150°F.
פלסטיקה הנדסית
The next level are the “Engineering” plastics which can be used for applications ranging up to 250°F. ABS is often considered an engineering plastic for its other properties although it cannot withstand this temperature level. For applications requiring temperature resistance up to 450°F, the next step, “Advanced Engineering,” is appropriate. The amorphous plastics at this level are often used in steam environments and the crystalline plastics have improved chemical resistance. The top level, the “Imidized” plastics, can withstand temperatures up to 800°F and have excellent stress and wear properties as well.




















השאר תגובה